 |
|
|

|
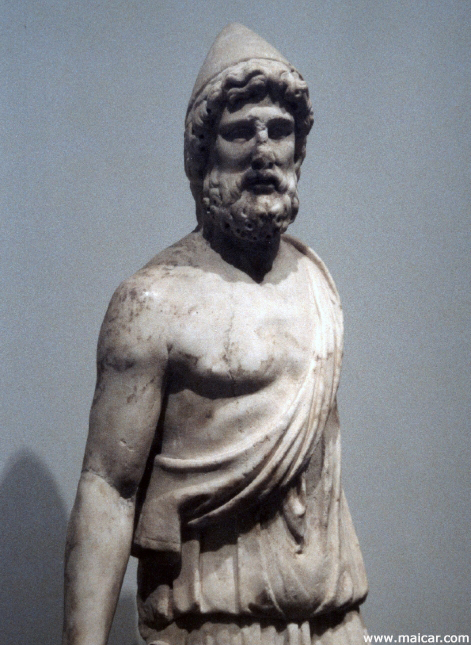
Hephaestus. 5814: Vulcain. IIe siècle après J.-C. Ostia Antica, Musée.
|
|
|
"A strangely potent tie is
kinship, and companionship as well." (Hephaestus. Aeschylus, Prometheus
Bound 39).
|
|
Hephaestus is the god of the smiths. He
discovered the ways of working iron, copper, gold,
silver, and everything else which requires fire for
working. Hephaestus is called son of Zeus and Hera. However, some say
that Hera, being angry at Zeus because he had
fathered Athena without
her participation, gave birth to Hephaestus alone.
If this is so then it was Prometheus 1, as
some say, and not Hephaestus, as others affirm, the
one who smote the head of Zeus with an axe in order
to let Athena be born
from the head of the god.
Chaining Prometheus 1
But it was Hephaestus, who following Zeus' instructions, chained Prometheus 1 to the
rock in Mount Caucasus with the help of Cratos
(Power) and Bia (Violence):
"Against my will, no less than yours, I must rivet you with brazen bonds … Such is the prize you have gained for your championship of man." (Hephaestus to Prometheus 1.
Aeschylus, Prometheus
Bound 20).
Hephaestus chained Prometheus 1 reluctantly:
Hephaestus: Oh
handicraft that I hate so much!
Cratos: Why hate it? Since in
truth your craft is in no way to blame for these
present troubles.
Hephaestus: Nevertheless, I
wish it had fallen to another's lot!
(Aeschylus, Prometheus
Bound 45).
Falls from heaven during a whole day
Hephaestus was lame in his legs because he fell
at sunset after a whole day fall on Lemnos when Zeus cast him out of
heaven. This happened because Hephaestus came to
the rescue of Hera when Zeus chained her because of
the storm she sent against Heracles 1 when the latter was at sea (see Lemnos, the island where Hephaestus is particularly worshipped.) But it is also said that it was Hera who cast him, not on Lemnos but on the sea,
because she was ashamed of her limping son. In
revenge, Hephaestus sent to Hera a golden chair with
invisible fetters and when she sat down she was
held fast. Some say that Dionysus 2 made him
drunk, and finally brought him back to Olympus.
|
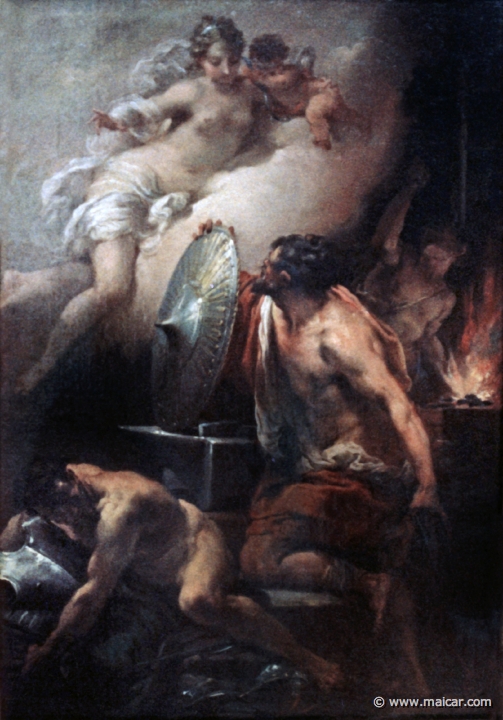
|
Aphrodite visiting Hephaestus in his smithy. 0830: Venus in Vulcan's workshop. Painting by Gaetano Gandolfi, 1734-1802. Staatsgalerie, Stuttgart.
|
|
Unhappy married
Hephaestus was married to Aphrodite, but she
loved Ares in the house of
Hephaestus whenever he was away. However,
Hephaestus, trapped the two lovers in bed with a
clever invention, and exposed them to the laughter
of the other OLYMPIANS. Later, Hephaestus attempted to have intercourse
with Athena when she came
to have new arms made by him. But she resisted him,
and the god dropped his seed on Athena's leg. And as she fled the seed fell on the ground, and Erichthonius 2 was born. Some affirm, however, that the mother of Erichthonius 2 was Gaia (see Offspring below).
Extraordinary works
Hephaestus made some extraordinary
constructions. He gave King Aeetes the brazen-footed
bulls that puffed fire from their mouths. He also
wrought the famous Necklace of Harmonia 1, and he made a bed forged of gold,
in which Helius (the Sun) is carried in sleep. Oenopion 1's underground house was also constructed by Hephaestus; and when Heracles 1 did not
know how to drive the Stymphalian Birds from the
wood, Athena gave him
brazen castanets to scared them with, which she had
received from Hephaestus. Hephaestus also made a scepter for Zeus, which the god gave to Hermes, Hermes to Pelops 1, Pelops 1 to Atreus, Atreus to Thyestes 1, and Thyestes 1 to Agamemnon (these are the Pelopides). This scepter is the only work considered to be authentic by Hephaestus. But others have shown bowls, and chests, falsified necklaces, and even temples, saying that Hephaestus had done them. But Hephaestus gave a golden breastplate to Heracles 1, and he
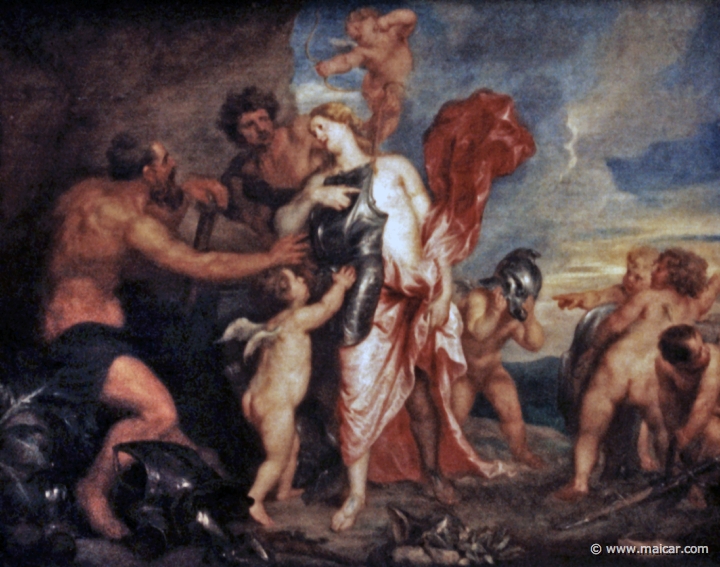
also made Achilles' new
armour, when he laid aside his wrath and decided to
return to the fight at Troy. And when Achilles killed
Asteropaeus, grandson of the river Axius, the river
god rushed at him, but Hephaestus dried up his
streams with a powerful flame.
A strange creature
Zeus gave Talos 1 to Europa to be the warder
of Crete, but this
creature made of bronze was, according to some, the
work of Hephaestus. Curiously enough, some have
represented Hephaestus as son of Talos 1, and Talos 1 as son of Cres. But, as it has been remarked: "The legends
of Greece generally have different forms, and this
is particularly true of genealogy." (Pausanias, Description
of Greece 8.53.5).
|
| Family |
Parentage (three versions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cabiro was a Thracian woman, daughter of Proteus 2.
Alcon 5 followed Dionysus 2 in his
Indian campaign.
Nonn.14.21, 17.195, 30.49.
|
|
|
The CORYBANTES,
the CABIROI, the DACTYLS and the TELCHINES are sometimes represented as
identical with the CURETES, and sometimes as
kinsmen of one another. Roughly speaking, they are
represented as a kind of inspired people, and as
subject to Bacchic frenzy, as inspiring terror at
the celebration of the sacred rites by means of
war-dances, noise and cymbals and drums and arms.
DH.1.23.5; Hdt.3.37; Nonn.14.19; Strab.10.3.21.
|
|
|
The NYMPHS CABIROIDES, were honoured in Lemnos. (See NYMPHS.).
Strab.10.3.21.
|
|
|
Strab.10.3.21.
|
|
|
Followed Dionysus 2 in his Indian campaign.
Nonn.14.21, 17.195.
|
|
|
|
Ardalus is said to be the inventor of the flute.
Pau.2.31.3.
|
|
|
|
A fire-breathing half-human creature who ate
human flesh and nailed the heads of men in the
doors of his cave. He was killed by Heracles 1.
DH.1.39.4; Ov.Fast.1.577; Prop.4.9.16; Vir.Aen.8.195ff.
|
|
|
|
The founder of Praeneste and an ally of Turnus
against Aeneas in Italy.
Vir.Aen.7.678, 10.543.
|
|
|
|
An Arcadian. He compelled passers-by to wrestle,
and in wrestling killed them. Theseus killed him and
ravished his daughter.
Apd.Ep.1.3; Dio.4.59.4; Hyg.Fab.38, 173, 187; Pau.1.14.3; Plu.The.11.1, 29.1.
|
|
|
|
Another evil-doer killed by Theseus. He carried a
club and with it killed anyone who passed by.
Dio.4.59.2; Hyg.Fab.38, 158.
|
|
|
|
This Caucasian eagle who devoured the liver of Prometheus 1 was
fashioned by Hephaestus, but some say it was the
offspring of Typhon & Echidna. The eagle was
killed by Heracles 1.
Apd.2.5.11; Dio.4.15.2; Hes.The.527; Hyg.Ast.2.15; Hyg.Fab.31; QS.10.200.
|
|
|
|
("a)", "b)", etc., stand for different versions). The lower part of Erichtohius 2's body was snakeformed. He became king of Athens after having
expelled Amphictyon.
Apd.3.14.6-7; Hyg.Ast.2.13; Hyg.Fab.48, 166; Eur.Ion.21; Pau.1.2.6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After him the city Olenus in Aulis was named.
Hyg.Ast.2.13.
|
|
|
|
One of the ARGONAUTS.
Apd.1.9.16; Hyg.Fab.14.
|
|
|
|
An evil-doer who carried a bronze club with
which he dispatched the passers-by. Killed by Theseus.
Apd.3.16.1; Plu.The.8.1.
|
|
|
|
Philammon was famous for his song and zither. He
was killed by an armed force of Phlegyans that
marched against the sanctuary at Delphi.
Apd.1.3.3; Hyg.Fab.158, 161, 200; Ov.Met.11.317; Pau.4.33.3, 9.36.2.
|
|
|
|
Hyg.Fab.158.
|
|
|
|
Rhadamanthys is one of the three JUDGES OF THE
DEAD.
Apd.2.4.11, 3.1.1-2; Hes.CW.19A; Hom.Od.4.564; Hyg.Fab.155; Lib.Met.33; Pau.7.3.6, 8.53.4-5; Pin.Oly.2.70.
|
|
|
|
Servius Tullius was King of Rome after
Tarquinius Priscus.
DH.1.75.2; Ov.Fast.6.624-627, 6.588.
|
|
|
|
Hyg.Fab.158.
|

Charis
|
|
Charis is one of the CHARITES.
|

Aglaia 1
|
|
One of the CHARITES.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
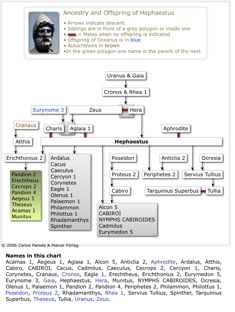
Genealogical Charts
Names in this chart: Acamas 1, Aegeus 1, Aglaia 1, Alcon 5, Anticlia 2, Aphrodite, Ardalus, Atthis, Cabiro, CABIROI, Cacus, Cadmilus, Caeculus, Cecrops 2, Cercyon 1, Charis, Corynetes, Cranaus, Cronos, Eagle 1, Erechtheus, Erichthonius 2, Eurymedon 5, Eurynome 3, Gaia, Hephaestus, Hera, Munitus, NYMPHS CABIROIDES, Ocresia, Olenus 1, Palaemon 1, Pandion 2, Pandion 4, Periphetes 2, Philammon, Philottus 1, Poseidon, Proteus 2,
Rhadamanthys, Rhea 1,
Servius Tullius, Spinther, Tarquinius Superbus, Theseus, Tullia, Uranus, Zeus. |
|
|

|
0536: Anton van Dyck 1599-1641. Thetis receives Achilles' new armour from Hephaestus. Künsthistorische Museum, Wien.
|
|
|
|
| Related sections |
OLYMPIANS
METAMORPHOSES |
|
|
Sources
Abbreviations |
Apd.1.3.5, 1.9.16, 3.14.6, 3.16.1;
Cal.Ze.75; Dio.5.74.2; Hes.The.929ff., 945;
Hom.Il.1.571, 18.382ff.; Hyg.Ast.2.13;
Hyg.Fab.38, 158; Nonn.14.21; Ov.Fast.6.627; Pau.1.2.6,
2.31.3, QS.2.139, Val.2.88; Vir.Aen.7.678, 8.195,
8.372.
|
|
|